If the stock is trading at $190 per share, the call owner buys Apple at $170 and sells the securities at the $190 market price. The break-even point (BEP) helps businesses with pricing decisions, sales forecasting, cost management, and growth strategies. A business would not use break-even analysis to measure its repayment of debt or how long that repayment will take. To calculate the Break-Even Point (Quantity) for which we have to divide the total fixed cost by the contribution per unit. Once the break-even number of units is determined, the company then knows what sales target it needs to set in order to generate profit and reach the company’s financial goals. The most important advantage to using the method is that it shows the minimally required amount of economic activity, necessary to prevent potential losses.
See profit at a glance
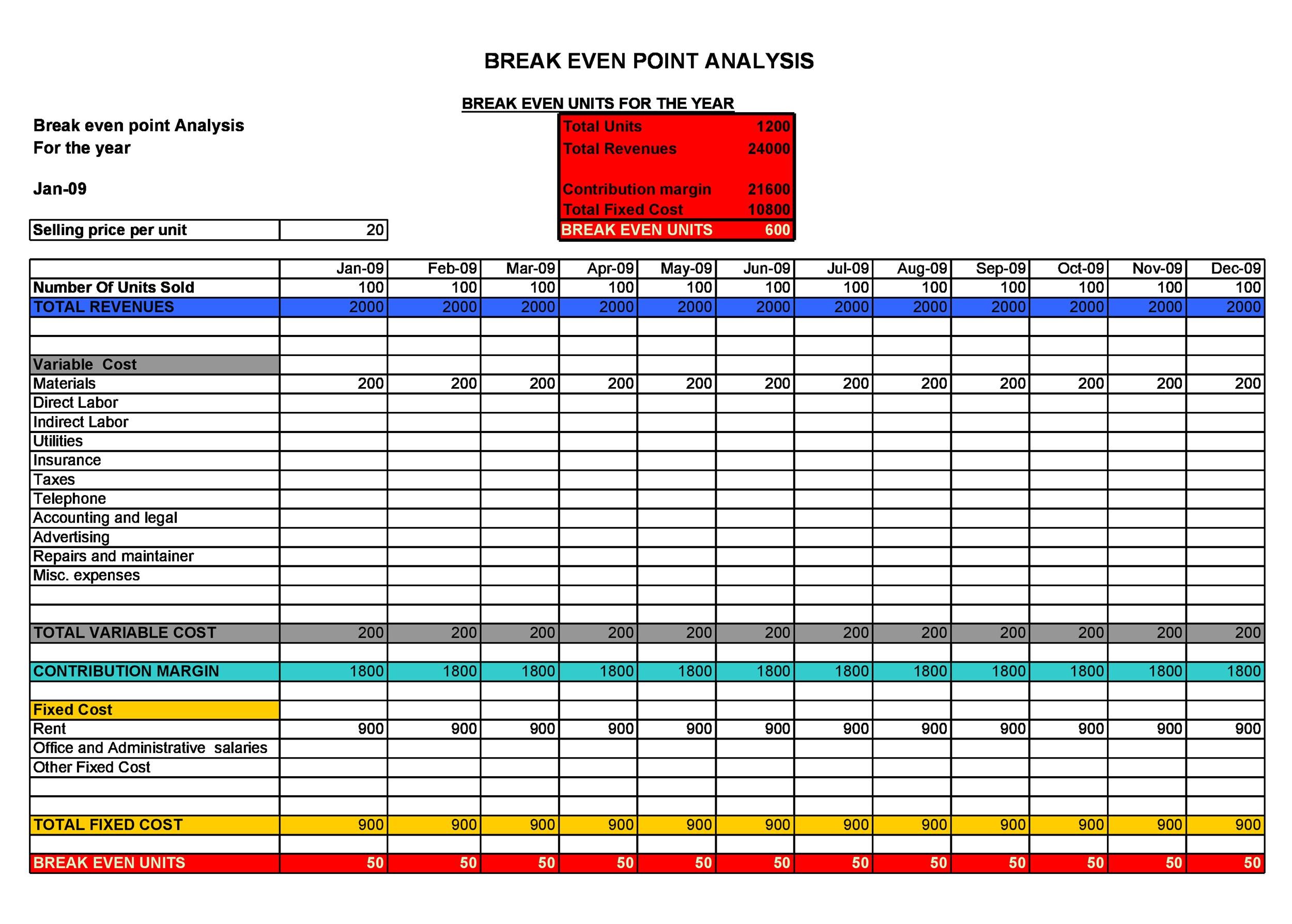
To find the total units required to break even, divide the total fixed costs by the unit contribution margin. Break-even analysis involves a calculation of the break-even point (BEP). The break-even point formula divides the total fixed production costs by the price per individual unit less the variable cost per unit. Break-even analysis compares income from sales to the fixed costs of doing business. The five components of break-even analysis are fixed costs, variable costs, revenue, contribution margin, and break-even point (BEP). In addition, you can calculate the Break Even Point (BEP), also known as the critical point.
Free Financial Modeling Lessons
This analysis shows that any money generated over $200,000 will be net profit. Penetration strategy is related to loss leader pricing, where a few products are priced exceptionally low to grab attention, but other products are still sold at full price. • It evaluates financial risk by highlighting how changes in sales, retail sales and use tax costs, or pricing impact profitability. Break-even analysis is a financial technique used to determine the level of sales needed for a business to cover all its costs and achieve a break-even point. In financial modeling, break-even analysis can be used to forecast future performance under different scenarios.
Changing the business model
- So, after deducting $10.00 from $20.00, the contribution margin comes out to $10.00.
- As for the business, entrepreneurs would learn how much investment they require to break even.
- This means that the only thing holding back your ability to break even is how fast you sell your units.
- Beyond this point, every additional unit sold or dollar of revenue generated will contribute to profit.
- The break-even point (BEP) is the point at which the costs of running your business equals the amount of revenue generated by your business in a specified period of time.
- However, if you want to bring your variable costs down, focus on enhancing operational efficiencies.
It can also hint at whether it’s worth using less expensive materials to keep the cost down, or taking out a longer-term business loan to decrease monthly fixed costs. That’s the difference between the number of units required to meet a profit goal and the required units that must be sold to cover the expenses. In our example, Barbara had to produce and sell 2,500 units to cover the factory expenditures and had to produce 3,500 units in order to meet her profit objectives.
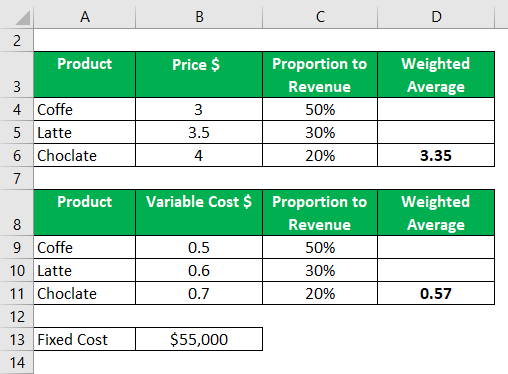
The contribution margin is the selling price of the product minus the total variable costs. Your selling price is usually the amount you place on any customer invoices. It is also possible to calculate how many units need to be sold to cover the fixed costs, which will result in the company breaking even.
Move, manage, and grow your money
Instead, use this exercise to understand potential pricing options and begin testing them with your target customers. In this guide, we’ll cover what a break-even point is, why it’s critical to calculate, how to calculate it, and additional factors you should consider. For instance, instead of purchasing expensive raw materials, you can negotiate better rates with suppliers by buying in bulk. Even better, you can source from local providers to reduce transportation costs. There are only two ways to reach your break-even faster—reduce the costs or raise the pricing.
Profitability may be increased when a business opts for outsourcing, which can help reduce manufacturing costs when production volume increases. When there is an increase in customer sales, it means that there is higher demand. A company then needs to produce more of its products to meet this new demand which, in turn, raises the break-even point in order to cover the extra expenses. The Break Even Analysis is a handy tool to decide if a company should or should not start producing and selling a product. When analyzing your break-even point, not only do you want to see that your business is breaking even, you’re looking to make sure your business is profitable as well. Here are a few ways to lower your break-even point and increase your profit margin.
So how do you calculate break-even points accurately and use them appropriately? To help you find the answers, here are some useful definitions and some strategies. Paul Boyce is an economics editor with over 10 years experience in the industry.
— e.g., changes in market demand, economic conditions, inflation, supply chain disruptions, etc. For instance, if shipping costs rise due to global supply chain problems, your variable costs might go up and can throw off your original calculation. Similarly, If a competitor starts offering big discounts, your projected sales might drop and may cause you to miss your break-even point. • Break-even analysis identifies the sales volume needed to cover total costs, helping businesses understand their required revenue to avoid losses. To get your contribution margin ratio, divide your contribution margin per unit with your average sales price.
To start and sustain a small business it is important to know financial terms and metrics like net sales, income statement and most importantly break-even point. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. It is only useful for determining whether a company is making a profit or not at a given point in time. Sales below the break-even point mean a loss, while any sales made above the break-even point lead to profits. In conclusion, just like the output for the goal seek approach in Excel, the implied units needed to be sold for the company to break even come out to 5k.








